are fungi eukaryotic
They have nuclei with well-defined chromosomes and nuclear walls and are often multicellular. Other than the moulds-which-arent-the-same-as-the-other-moulds fungi mushrooms fungus most molds yeast etc are eukaryotes.
 |
| Procaryote And Eukaryote Comparision Prokaryotes Cells Worksheet Biology Worksheet |
Fungi are Eukaryotic organisms.

. Some eukaryotic fungi examples are mushrooms molds yeasts truffles etc. Are fungi prokaryotic organisms. A eukaryotic protist or a cyanobacter a prokaryotic protist. They are classified as heterotrophs among the living organisms.
Lichens further complicate it by being a symbiotic species consisting of fungi and a photosynthetic partner either a chlorophyta green algae. All of the following statements about helminths are true except. Fungi are eukaryotic organisms. The fungi are one of the 4 eukaryotic kingdoms.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that comprise one of the kingdoms of life. The organisms found in Kingdom fungi contain a cell wall and are omnipresent. Fungi is a Eukaryotic Organisms because the cells of Fungi have a definite nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane and organelles such as mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum Golgi bodies etc. Fungi are a distinct kingdom of eukaryotic or prokaryotic mostly multicellular organisms that lack chlorophyll.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include microorganisms such as yeasts moulds and mushrooms. They are predominantly multicellular and some are unicellular yeast. Take in food molecules by absorption. Like plants fungi have a cell wall but it is made up of chitin and they do not possess chloroplasts.
Being a microscopic organism fungi have a complex cellular organization like a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins and so they are considered eukaryotic organisms. Reproductive types are important in distinguishing fungal groups. Fungi can be unicellular or multicellular. There are many thousands of different fungi that share our environment and we are constantly being exposed to fungi in the air we breathe the food we eat and the water we drink.
As eukaryotic organisms fungi possess cells with organelles which are structures surrounded by membranes. Some like yeast and fungal spores are microscopic whereas some are large and conspicuous. Ie their cells contain membrane-bound organelles and clearly defined nuclei. However they are also responsible for some.
Fungi are eukaryotes and have a complex cellular organization. Few fungi are pathogenic to humans. Fungi bind soil together by their filamentous form exudates and trophic interactions with all other groups of soil organisms. Answer 1 of 6.
This chapter provides an overview of fungi and eukaryotic algae as both these groups share a range of morphologiesthat is from filamentous to cellular. Fungi is a type of eukaryotic organism belonging to the kingdom Fungi alongside plants animals protozoa and monera. As eukaryotes fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins. They are heterotrophic b.
They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota. They possess a membrane bound eukaryotic kind of well organized cell structure also having a member bound proper nucleus in it. No - fungi are eukaryotic. These organisms are classified under kingdom fungi.
Fungi are eukaryotes and have a complex cellular organization. Most fungi are multicellular. A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids loops of DNA. In contrast their DNA matches the maximum with animals.
Historically fungi were included in the plant kingdom. Eukaryotic organisms have a nucleus and membrane-boun organelles. Fungi are heterotrophic d. Fungi have these - and so are not prokaryotic.
Here Lets know about eukaryotic organisms in detail. All fungi have eukaryotic cells c. Like plants they have cell walls but unlike plants the walls contain chitin and the cells do not contain chloroplasts. Most fungi are aerobic e.
A fungus plural. Most are multicellular but there are some single-celled types as well yeasts. Which includes the yeasts rusts smuts mildews molds and. Fungus are a kingdom of usually multicellular eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophs cannot make their own food and have important roles in nutrient cycling in an ecosystem.
As eukaryotes fungal cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus where the DNA is wrapped around histone proteins. They are multicellular animals c. They can maintain different environments in a single cell that allows them to carry out various metabolic reactions. Fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually and they also have symbiotic associations with plants and bacteria.
A few types of fungi have structures comparable to bacterial plasmids loops of DNA. Protozoa fungi plants and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They have eukaryotic cells. Grow on and through their food and secrete digestive enzymes - external digestion.
Eukaryotic cells arose from prokaryotic cells and have a more complex organization than prokaryotic cells. However because fungi lack chlorophyll and are distinguished by unique structural and physiological features ie components of the cell wall and cell membrane they have been separated from plants. Fungi are enormously important in carbon. The fungi include diverse saprotrophic eukaryotic organisms with chitin cell walls.
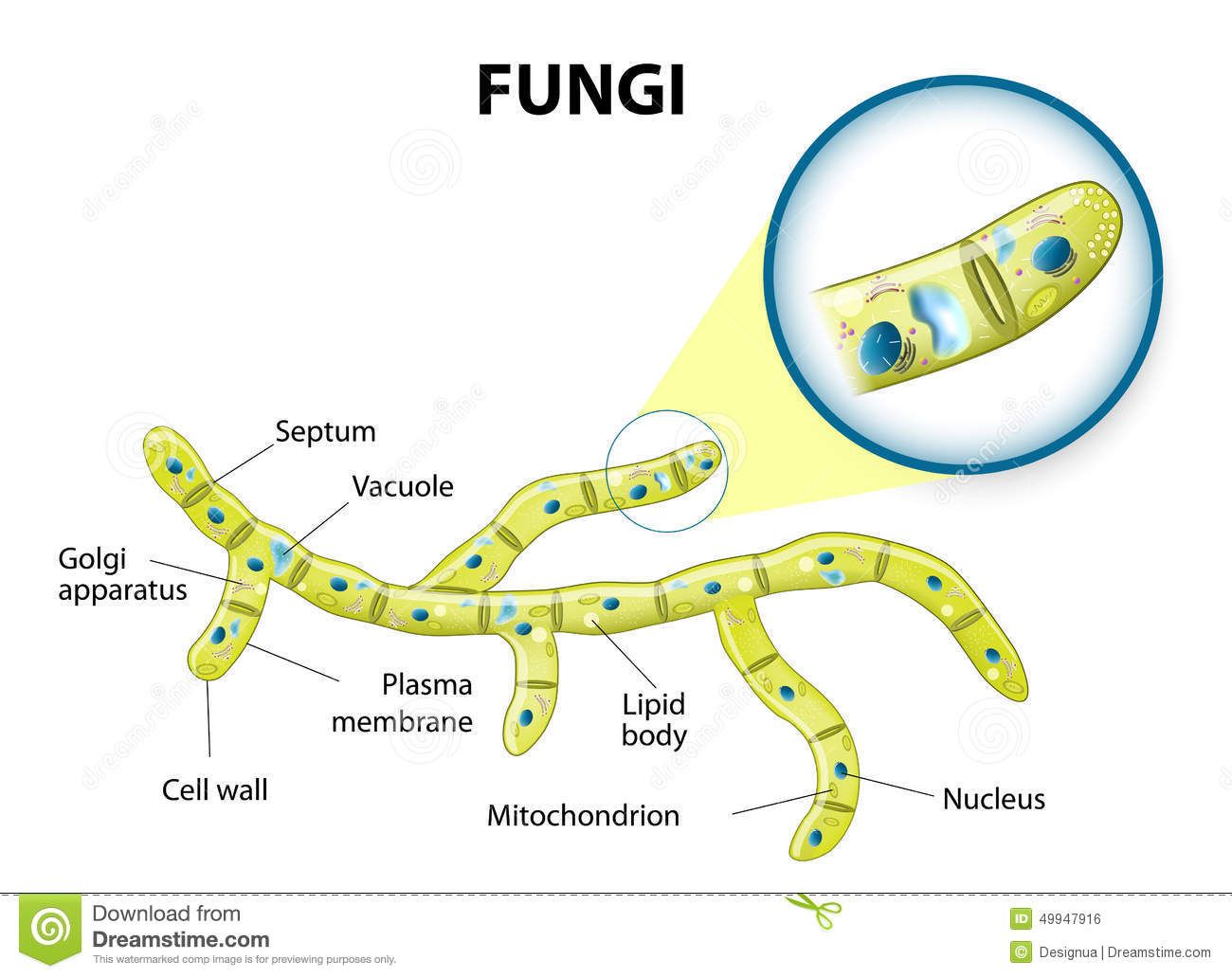 |
| Fungi Cell Stock Vector Illustration Of Life Herbal 49947916 Fungi Cell Diagram Eukaryotic Cell |
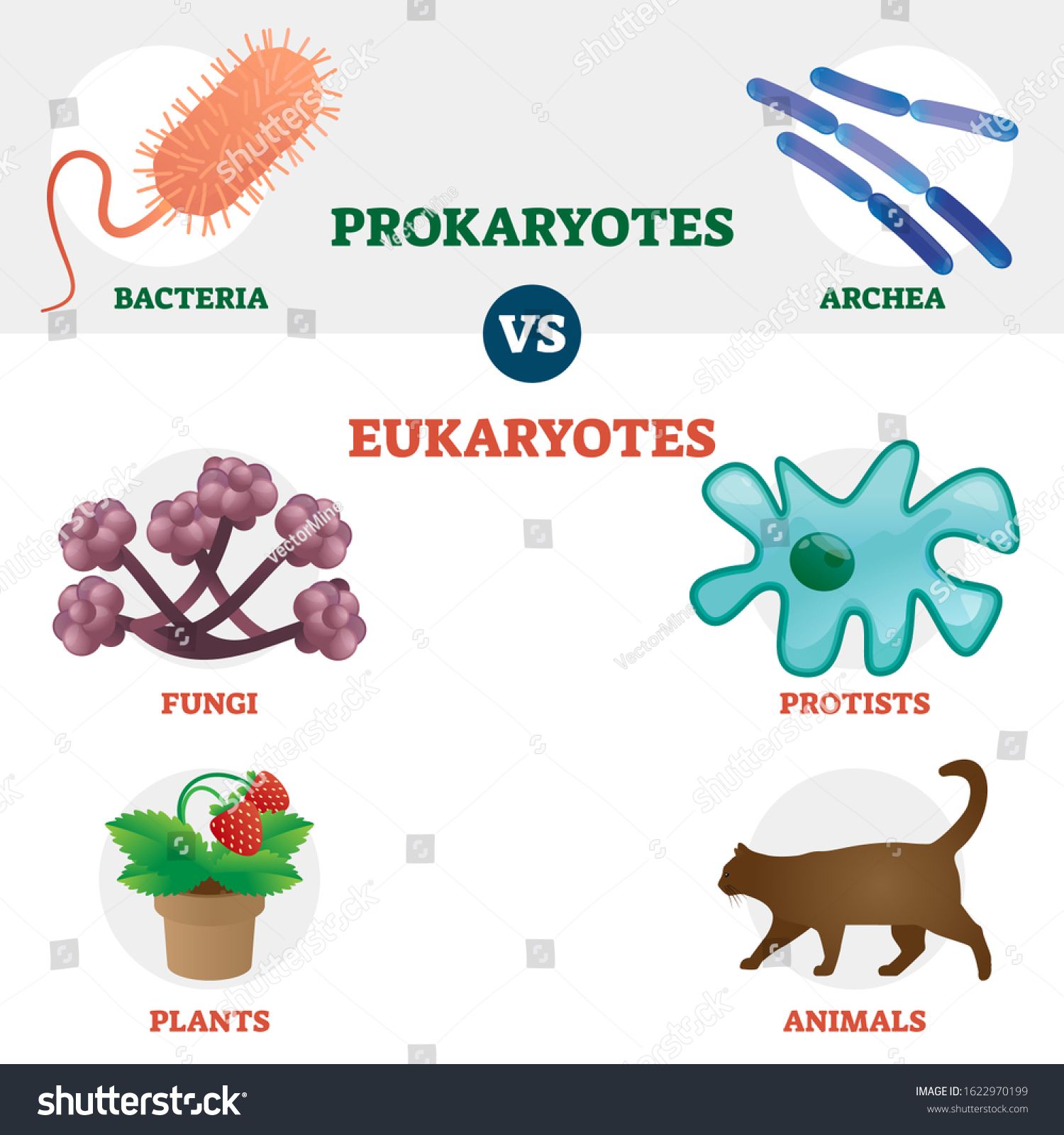 |
| Eukaryote Vs Prokaryote Cell Type Organisms Educational Set With Bacteria Archea Fungi Protists Pla Prokaryotes Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes Prokaryotic Cell |
 |
| 6 Differences Between Plant Cell And Fungal Cell Simple Point Wise Explanation Plant Cell Cell Wall Teaching Biology |
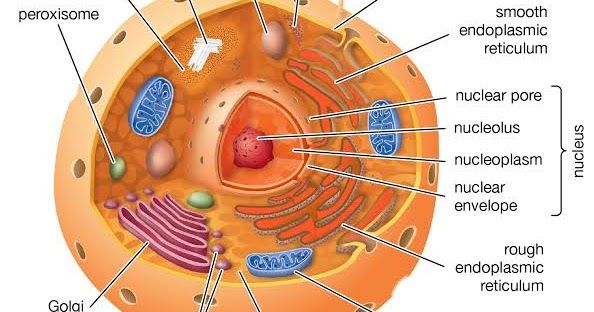 |
| Eukaryotes Comprise All Members Of Plantae Fungi And Animal Kingdomsincluding The Unicellular Fungus Yeast And Protozoans E Sel Hewan Membran Sel Dinding Sel |
 |
| Prokaryotic Cell Vs Eukaryotic Cell By Nadiadaniela Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell Prokaryotes |
Posting Komentar untuk "are fungi eukaryotic"